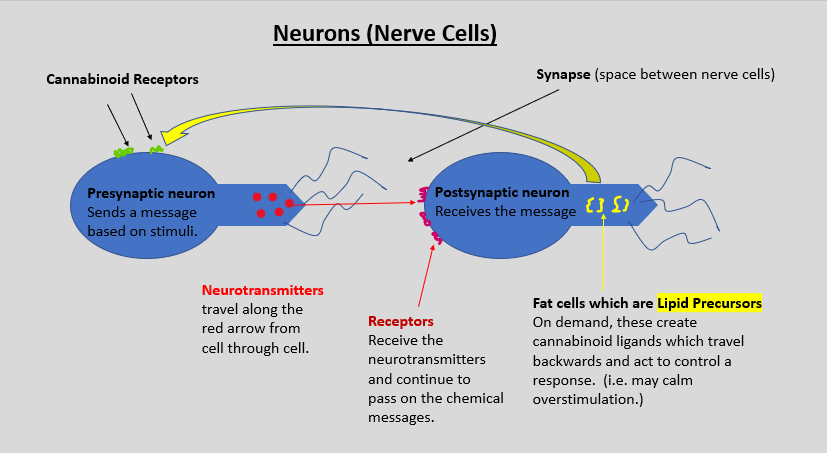
 We've been exploring products made from industrial Hemp -- so far, Hemp Seed Oil and Hemp Essential Oil. Logically, the next item is CBD, but before we dive into CBD, it's important to understand the Human Endocannabinoid System. If you studied basic health in school, you learned that we have several systems in our bodies. They include the respiratory system, endocrine system, cardiovascular system, digestive system, nervous system, and (discovered in the 1990's) the Human Endocannabinoid System (ECS). That's right, our bodies have their own cannabinoid system (as do all vertebrates). In one of my herbal courses, the professor referred to the digestive system as as a "second brain" because of its autonomy in function. Based on what I've learned, I think I would refer to the ECS as a 'third brain'. I say this because our ECS is designed to know when something (anything) in the body gets out of balance, and then signal the appropriate mechanisms to initiate procedures which will return the body to a balanced state. What are the components of the Endocannabinoid System? First, within the cells of our nervous system, there are molecules which bind to proteins. These molecules are called ligands. The function of a ligand is to initiate a signal response. Anandamide (AEA), 2-arachidonoylgycerol (2-AG), N-arachidonoyldopamine (NADA), Virodhamine (EOE), and noladin ether are endocannabinoid ligands found in the nervous system. Next, there are receptor cells called CB1 and CB2. receptors. CB1 receptors are found primarily in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), and CB2 receptors are found in the peripheral nervous system (everything outside of the brain and spinal cord) with a large concentration found in our immune cells. They receive the ligands like a catcher's mitt receives a pitched ball. Enzymes called Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) break down the ligands when they are no longer needed. Now we know what the ECS is made of, how do these parts work in our bodies? In the illustration above, we see (my rendition) of two nerve cells. In a normal process, the presynaptic neuron receives some kind of stimulus. It then sends neurotransmitters (chemical and electrical messengers) to the next cell (called the postsynaptic neuron). Each cell then passes those messengers through to the next cell in the nerve pathway until the message gets to the spinal cord where it is passed up to the brain. Sometimes, a nerve cell gets overstimulated. One example of this would be in the case of acute injury. The nerve cells send a message to the brain to send immune cells to the site of injury to start the repair process. Those immune cells then trigger the neurons to send more immune cells. The signaling for more and more immune cells would continue without stopping except that the body has a mechanism to recognize when to halt the signaling and calm down the neurons. Otherwise, an injury would continue to swell out of control. This is where the Endocannabinoid System kicks in. Fat cells in the postsynaptic neuron create cannabinoid ligands and send them backwards to the synapse. From there, the ligands attach to a CB receptor on the presynaptic neuron and 'calm down' the messaging activity. Once balance is achieved, the ligands are no longer needed, so the FAAH and MAGL enzymes break down the ligands. This sounds simple, but billions of neurotransmitters are being sent through our nervous system every day, so our ECS is constantly relied upon to maintain balance in every part of our bodies. It helps regulate the immune system, sleep, reproduction, focus, memory, pain, inflammation, digestion, brain chemistry, mood/attitude, gross and fine motor control, bone health, sensitivity to heat and cold, etc. What happens if the ECS gets out of balance? An out-of-balance or malfunctioning Endocannabinoid system can be a big problem and lead to many chronic diseases like fibromyalgia, IBS, migraines, anxiety, and even chronic pain that continues after an injury has healed. Poor diet and lifestyle may cause deficiencies in the ECS. Such deficiencies may be a significant factor in feelings of chronic fatigue and depression. Scientists are studying all of this to try and understand more clearly just how much of an impact our EC system has on our overall health. Remember, this system was only discovered 20 - 30 years ago, so what we do know is far less than what we don't know. Many studies being performed are trying to determine how phytocannabinoids, like CBD, and terpenes that act like cannabinoids (i.e. beta-caryophyllene) interact with the ECS and how they can be used to support it. Next week's blog will discuss what scientists have learned about CBD and its impact on the Human Endocannabinoid System. Sources: 1. UCLA Health: Cannabis Research Initiative, Human Endocannabinoid System, UCLA Health, https://www.uclahealth.org/cannabis/human-endocannabinoid-system Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 2. Maimonides, Rambam, The Endocannabinoid System, Cannabinoids, and Pain, NCBI, Medical Journal PMCID: PMC3820295, Published online Oct 29, 2013 doi: 10.5041/RMMJ.10129, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3820295/ Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 3. Scholastic, The Science of the Endocannabinoid System: How THC Affects the Brain and the Body, First published 2011, http://headsup.scholastic.com/students/endocannabinoid Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 4. Dellwo, Adrienne, What is the Endocannabinoid System: How the system works and its role in disease, verywell health, Updated April 26, 2019, https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-is-the-endocannabinoid-system-4171855 Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 5. Sulak, Dustin, DO, Healer.com, Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System, NORML, Copyright 2019, https://norml.org/library/item/introduction-to-the-endocannabinoid-system, Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 6. CBD OIL review, Endocannabinoid Production in the Human Body, Copyright 2018, https://cbdoilreview.org/cbd-cannabidiol/cbd-oil-endocannabinoid-production-human-body/, Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 7. wiseGEEK, What is the Endocannabinoid System, Copyright 2003 - 2019, https://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-the-endocannabinoid-system.htm Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 8. Trent, Stacy, The Endocannabinoid System [Explained], NaturalWellness CBD Oil, Updated July 8, 2018, https://naturalwellnesscbdoil.com/blog/the-endocannabinoid-system-explained/, Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 9. Leaf Science Team, The Endocannabinoid System: A Beginner's Guide, leaf science, March 17, 2017, https://www.leafscience.com/2017/03/17/the-endocannabinoid-system-a-beginners-guide/, Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 10. Sandro, Pietraszko, What is the Endocannabinoid System? Human Cannabinoid System, The Hemp Cannabinoid Oil Benefits: Information Platform, February 11, 2018, https://thehempoilbenefits.com/what-is-the-endocannabinoid-system-2, Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 11. CBD School, The Endocannabinoid System Explained, CBD School, May 17, 2017, https://www.cbdschool.com/the-endocannabinoid-system-explained/ Accessed July 22 - 23, 2019 Comments are closed.
|
Archives
February 2021
CategoriesAuthorKaren Dragoo |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed